Management Accounting and Financial Accounting serve unique roles in business operations. Fiscal Accounting, handled by financial accountants, involves recording and reporting historical financial data accurately for external stakeholders. On the other hand, Management Accounting, managed by managerial accountants, focuses on internal strategies, problem-solving, and long-term business success to enhance profitability.
At SAS KPO Services we offer outsourcing solutions tailored to meet the distinct needs of both fields, ensuring accurate financial reporting and strategic management for your business’s success. Our team of experts utilises strategic plans to assess the overall operational strategy within your organisation, empowering you to make sound business decisions and drive success.
What is Management Accounting and Financial Accounting

Management accounting, also known as managerial accounting, is the process of setting organisational goals by collecting, analysing, and communicating information to managers. It focuses on providing insights into operational metrics, such as the costs of products or services purchased by the company. Budgets are commonly used to plan operations, and management accountants use performance reports to identify differences between actual results and budgeted figures. Essentially, management accounting helps managers make decisions that benefit the organisation by creating statements, reports, and documents related to business performance. It is used internally to aid in achieving business objectives.
Financial Accounting is a specialised field of accounting focused on recording, summarising, and reporting business transactions over a specific period. These transactions are then used to prepare financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which provide insights into a company’s financial performance. In simpler terms, financial accounting involves analysing and summarising financial transactions related to a business. This includes preparing financial statements that are available for public use. Various stakeholders, such as stockholders, suppliers, banks, employees, government agencies, and business owners, use this information to make decisions. Financial accounting follows both local and international accounting standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards provide a framework of guidelines for recording, summarising, and preparing financial statements in any given command.
Additionally, the reports generated in management accounting and financial accounting are based on the same database, originally created to meet financial accounting’s reporting requirements. This is why the accounting system in an organisation collects and categorises information in a format suitable for both accounting systems. They both offer insights into a company’s financial performance.
Goals of Management Accounting and Financial Accounting

The objectives of management accounting and financial accounting contribute to the effective management and financial well-being of businesses, ensuring transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making.
Management Accounting
Decision Making:
Management accounting helps managers make better decisions by providing detailed insights into various financial aspects. It assists in choosing between alternative strategies, assessing investment opportunities, and determining the most efficient use of resources. This enables businesses to navigate through complex decisions with precision, both operationally and strategically.
Planning:
Planning is a strategic objective of management accounting, involving setting goals and outlining steps to achieve them. By analysing historical data and market trends, management accounting provides forecasts, ensuring businesses have long-term strategies and short-term plans. This critical process is essential for resource allocation, setting financial targets, and preparing for future growth.
Controlling Business Operations:
Another fundamental objective is controlling business operations, which entails monitoring performance against established benchmarks and implementing corrective measures when variations happen. Through techniques like budgetary control and variance analysis, management accounting identifies areas where performance is requiring, allowing for timely adjustments to optimise efficiency and maintain financial discipline.
Organising Business Processes:
Organising focuses on structuring business processes and resources efficiently. Management accounting identifies key profit and cost centers, facilitating effective resource allocation and departmental accountability. This structured approach ensures resources are utilised where they can generate the most value, enhancing financial health and operational effectiveness.
Understanding Financial Data:
Managerial accounting aims to make complex financial data accessible and understandable to non-financial managers. By translating involve financial statements into clear insights, it enables managers to participate more actively in financial planning and analysis, identify cost-saving opportunities, and better manage resources.
Identifying Business Problem Areas:
Identifying problem areas within the business involves exploring financial and operational data to pinpoint inabilities and areas not positioning with financial goals. Management accounting guides managers in focusing improvement efforts where they are most needed, ensuring businesses can adapt to challenges and enhance performance continuously.
Strategic Management:
Strategic management aligns financial analysis and planning with the company’s long-term vision and goals. Management accounting supports this process by offering insights into market trends, competitive moves, and internal abilities. It facilitates the implementation of strategic plans by translating them into financial and operational objectives.
Providing and Analysing Data:
Management accounting gathers comprehensive financial and operational data, offering a detailed view of the company’s performance. Through analysis, it identifies trends, assesses financial health, and uncovers insights that guide decision-making, ensuring strategies are developed with a clear understanding of their potential impact.
Financial Accounting
Recording Financial Transactions:
Fiscal accounting aims to accurately record all financial activities of a business, such as sales, purchases, expenses, and revenues. The goal is to maintain a systematic record of these transactions.
Preparing Financial Statements:
Another objective is to summarise the recorded financial data into statements like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These statements provide a snapshot of the company’s financial performance and position, helping stakeholders understand its financial health.
Providing Information for Decision-Making:
Financial accounting provides relevant financial information to stakeholders like investors, creditors, and managers. Consequently this helps them make informed decisions regarding investments, lending, strategic planning, and day-to-day operations.
Ensuring Accountability and Transparency:
Year end accounting ensures that businesses follow standardised accounting principles, promoting accountability and transparency in financial reporting. This builds trust among stakeholders and the public, maintaining investor confidence and ethical business practices.
Assessing Financial Health:
Through analysis of financial statements, financial accounting values the financial health of a business, including its liquidity, solvency, profitability, and efficiency. This helps stakeholders understand the company’s ability to generate profits, meet obligations, and sustain operations.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements:
Financial accounting ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, including tax obligations, financial regulations, and statutory filing requirements. Accurate reporting helps avoid legal penalties and supports moral financial management practices.
Facilitating Rational Decision-Making:
Monetary accounting contributes to informed economic decision-making by providing clear insights into a business’s financial performance and position. This supports efficient resource allocation, investment decisions, and overall economic stability and growth.
Differences Between Management Accounting and Financial Accounting
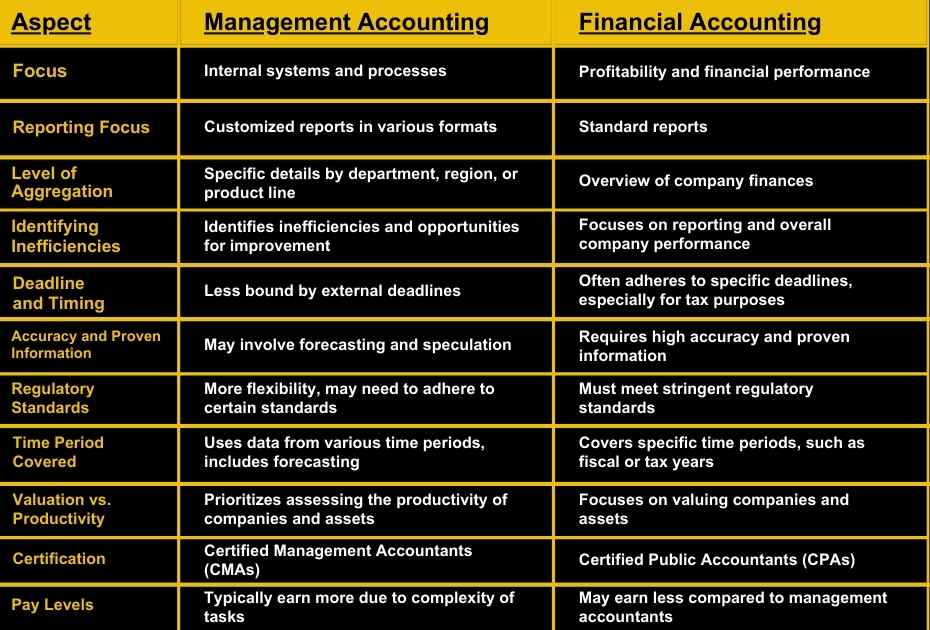
Focus on Internal Systems vs. Financial Performance:
Management accounting focuses on internal systems and processes to streamline operations and maximise efficiency.
Monetary accounting is centered around assessing the profitability and financial performance of a business.
Reporting Focus:
Financial accounting typically produces standard reports, while management accounting often requires specialised reports in various formats.
Level of Aggregation:
Year end accounting provides an overview of a company’s finances, while management accounting delves into specific details by department, region, or product line.
Identifying Inefficiencies and Opportunities:
Analytical accounting not only assesses financial efficiency but also identifies inabilities and opportunities for improvement.
Deadline and Timing:
Financial accounting often adheres to specific deadlines, especially for tax purposes.
Managerial accounting is less bound by external deadlines and can be produced over longer periods or on short notice as needed.
Accuracy and Proven Information:
Financial accounting requires high accuracy and proven information since reports are used by external parties and authorities.
Management accounting may involve prediction and opinion, which are basically less precise.
Regulatory Standards:
Financial accounting reports must meet stringent regulatory standards due to external use.
Cost accounting reports have more flexibility but may still need to attach to certain standards.
Time Period Covered:
Financial accounting reports cover specific time periods, such as fiscal or tax years.
Administrative accounting may use data from various time periods and includes forecasting.
Valuation vs. Productivity:
Financial accountants focus on valuing companies and assets.
Management accountants prioritise assessing the productivity of companies and assets.
Certification:
Financial accountants are often Certified Public Accountants (CPAs), while management accountants may be Certified Management Accountants (CMAs).
Pay Levels:
Management accountants typically earn more than financial accountants due to the complexity of their tasks.
By understanding these differences, businesses can leverage both Analytical Accounting and Monetary Accounting to make informed decisions and drive success.
Advantages of Outsourcing Management Accounting and Financial Accounting

Access to Expertise:
Outsourcing your accounting functions provides access to specialised knowledge and highly trained professionals. These experts focus solely on financial and accounting tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in handling your company’s finances.
Cost Savings:
By outsourcing, you can reduce costs associated with hiring and maintaining in-house accounting staff, such as salaries, benefits, and taxes. Outsourced firms offer efficient services at competitive rates, leading to significant cost savings for your business.
Avoidance of Turnover and Time-off Issues:
Outsourcing eliminates concerns related to staff turnover, sick leave, and vacations. External accounting firms manage their team’s availability and ensure seamless continuity of services, relieving you of the burden of staffing disruptions.
Time Savings:
Outsourcing accounting tasks frees up time for business owners to focus on basic activities like marketing, sales, and operations. You no longer need to oversee accounting employees or provide guidance, allowing you to allocate your time more efficiently.
Flexibility to Meet Business Needs:
Outsourcing provides flexibility to scale up or down based on your business’s changing needs. You can easily adjust the level of accounting support required as your business grows or experiences changes in workload.
Ability to Scale Up or Down Quickly:
Outsourcing allows for swift scalability, enabling your business to handle increased workloads during peak periods without the need for hiring additional staff. Conversely, you can scale back during slower periods to optimise resources and reduce costs.
Access to Advanced Tools and Processes:
Outsourced firms utilise advanced tools and processes that may not be suitable for small businesses to implement independently. By using these resources, you can improve efficiency, streamline operations, and enhance overall performance.
Business Intelligence:
Outsourcing accounting provides valuable business intelligence and insights to support strategic decision-making. With access to comprehensive financial data and analysis, you can make informed decisions to drive growth and achieve your business goals effectively.
Overall, outsourcing management accounting and financial accounting functions offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, access to expertise, flexibility, and enhanced business intelligence. By partnering with SAS KPO Services, you can optimise your financial processes and focus on driving business success.
Conclusion-
Outsourcing managerial accounting and fiscal accounting functions can significantly benefit businesses in terms of cost savings, access to expertise, flexibility, and improved business intelligence. At SAS KPO Services, we understand the importance of accurate financial reporting and strategic management for business success. On the whole our team of experts is dedicated to providing tailored outsourcing solutions to meet the unique needs of your organisation.
Contact us today to experience the best outsourcing services and take your business to new heights.
Shivani Soni (Digital Marketing Specialist, Top Marketing Voice) writes this blog

